UVGUI动态内存分配实现原理
@firestaradmin 2020年10月16日22:10:34
UVGUI 动态内存分配实现原理
UVGUI的动态内存管理是仿照LVGL写的,这里做一下记录。
一、数据结构分析
UVGUI的动态内存管理,是通过一个入口结构体进行管理和分配,其内存块由 ug_mem_ent_t 结构体表示。定义如下:
#define MEM_UNIT uint32_t
/*The size of this union must be 4 bytes (uint32_t)*/
typedef union {
struct {
MEM_UNIT used : 1; /* 1: if the entry is used*/
MEM_UNIT d_size : 31; /* Size off the data (in bytes)*/
} s;
MEM_UNIT header; /* The header (used + d_size)*/
} ug_mem_header_t;
typedef struct {
ug_mem_header_t header;
uint8_t first_data; /*First data byte in the allocated data (Just for easily create a pointer)*/
} ug_mem_ent_t;其中 有一些定义:
MEM_UNIT为内存最小单位,主要根据系统位数决定。如32位系统一般使用uint32_t。ug_mem_header_t联合为内存头信息。表示该内存块是否被使用以及内存块大小。ug_mem_ent_t为内存块的入口结构体,其包含一个内存头信息,和一个char类型的变量first_data,first_data只是为了方便创建指针指向内存块储存区域的首地址。
内存基本结构图如下:
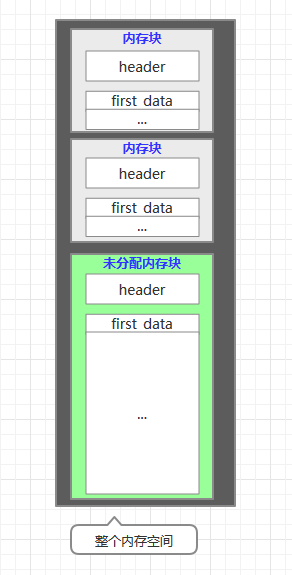
UVGUI的内存是一块一块的,每一块内存的起始处,有一个头信息union header 来表示该内存块是否被使用,已经该内存块的大小。
系统刚开始运行,没有申请过内存,则整个内存池就是一个内存块,该内存块的头信息的used 属性为0,表示未被使用,d_sized 属性为整个内存池的大小减去头信息的大小,即为内存池可用空间。
二、初始化
初始化函数 void _ug_mem_init(void);
申请一个指定大小的数组,用于分配内存块。
用work_mem指针储存内存池的首地址,用变量mem_max_size追踪内存堆中申请过的最大内存大小。
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0 static uint8_t * work_mem; #endif #if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0 static uint32_t mem_max_size; /*Tracks the maximum total size of memory ever used from the internal heap*/ #endif初始化内存池的首个入口,将used属性设为0,并且更新内存池可用大小至首个入口的d_size属性中。
/**
* Initialize the dyn_mem module (work memory and other variables)
*/
void _ug_mem_init(void)
{
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
/*Allocate a large array to store the dynamically allocated data*/
static UG_MEM_ATTR MEM_UNIT work_mem_int[UG_MEM_SIZE / sizeof(MEM_UNIT)];
work_mem = (uint8_t *)work_mem_int;
mem_max_size = 0;
ug_mem_ent_t * full = (ug_mem_ent_t *)work_mem;
full->header.s.used = 0;
/*The total mem size id reduced by the first header and the close patterns */
full->header.s.d_size = UG_MEM_SIZE - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t);
#endif
}三、API 接口
1|申请内存
申请内存,由如下函数实现:
/**
* Allocate a memory dynamically
* @param size size of the memory to allocate in bytes
* @return pointer to the allocated memory
*/
void * ug_mem_alloc(size_t size)
{
if(size == 0) {
return &zero_mem;
}
#ifdef UG_ARCH_64
/*Round the size up to 8*/
size = (size + 7) & (~0x7);
#else
/*Round the size up to 4*/
size = (size + 3) & (~0x3);
#endif
void * alloc = NULL;
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
/*Use the built-in allocators*/
ug_mem_ent_t * e = NULL;
/* Search for a appropriate entry*/
do {
/* Get the next entry*/
e = ent_get_next(e);
/*If there is next entry then try to allocate there*/
if(e != NULL) {
alloc = ent_alloc(e, size);
}
/* End if there is not next entry OR the alloc. is successful*/
} while(e != NULL && alloc == NULL);
#endif /* UG_MEM_CUSTOM */
if(alloc == NULL) {
//TODO: LOG("Couldn't allocate memory");
}
else {
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
/* just a safety check, should always be true */
if((uintptr_t) alloc > (uintptr_t) work_mem) {
if((((uintptr_t) alloc - (uintptr_t) work_mem) + size) > mem_max_size) {
mem_max_size = ((uintptr_t) alloc - (uintptr_t) work_mem) + size;
}
}
#endif
}
return alloc;
}void * ug_mem_alloc(size_t size) 函数申请指定大小的内存块,先将大小四字节对齐(32位系统下),然后申请一个入口结构体指针e,循环使用e = ent_get_next(e) 获取下一个入口地址,然后在ent_alloc 这个函数中做真正的内存申请,直到找不到一下个入口或者成功申请到内存。
判断内存块是否被使用和大小是否足够,是在ent_alloc 这个函数中判断的,具体请继续往下看。
ent_get_next 函数如下:
/**
* Give the next entry after 'act_e'
* @param act_e pointer to an entry
* @return pointer to an entry after 'act_e'
*/
static ug_mem_ent_t * ent_get_next(ug_mem_ent_t * act_e)
{
ug_mem_ent_t * next_e = NULL;
if(act_e == NULL) { /*NULL means: get the first entry*/
next_e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)work_mem;
}
else { /*Get the next entry */
uint8_t * data = &act_e->first_data;
next_e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)&data[act_e->header.s.d_size];
if(&next_e->first_data >= &work_mem[UG_MEM_SIZE]) next_e = NULL;
}
return next_e;
}每次申请内存时,都是从第一个入口开始往后寻找。
ent_alloc 函数如下:
/**
* Try to do the real allocation with a given size
* @param e try to allocate to this entry
* @param size size of the new memory in bytes
* @return pointer to the allocated memory or NULL if not enough memory in the entry
*/
static void * ent_alloc(ug_mem_ent_t * e, size_t size)
{
void * alloc = NULL;
/*If the memory is free and big enough then use it */
if(e->header.s.used == 0 && e->header.s.d_size >= size) {
/*Truncate the entry to the desired size */
ent_trunc(e, size);
e->header.s.used = 1;
/*Save the allocated data*/
alloc = &e->first_data;
}
return alloc;
}判断该内存块入口是否被使用以及大小是否足够用于申请内存,如果满足条件,则使用函数ent_trunc() 函数将此入口截断,然后返回申请的内存的储存首地址(即该内存块的头信息后的用户真正可以使用的储存首地址)。如果不满足条件,则返回NULL;
ent_trunc() 函数如下:
/**
* Truncate the data of entry to the given size
* @param e Pointer to an entry
* @param size new size in bytes
*/
static void ent_trunc(ug_mem_ent_t * e, size_t size)
{
#ifdef UG_ARCH_64
/*Round the size up to 8*/
size = (size + 7) & (~0x7);
#else
/*Round the size up to 4*/
size = (size + 3) & (~0x3);
#endif
/*Don't let empty space only for a header without data.
如果分配后只剩仅能保存一个头部的内存,那么就直接全部分配给这个内存块*/
if(e->header.s.d_size == size + sizeof(ug_mem_header_t)) {
size = e->header.s.d_size;
}
/* Create the new entry after the current if there is space for it */
if(e->header.s.d_size != size) {
uint8_t * e_data = &e->first_data;
ug_mem_ent_t * after_new_e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)&e_data[size];
after_new_e->header.s.used = 0;
after_new_e->header.s.d_size = (uint32_t)e->header.s.d_size - size - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t);
}
/* Set the new size for the original entry */
e->header.s.d_size = (uint32_t)size;
}该函数根据需要申请的内存大小截断内存块的数据区,将原来的内存块截断为两块,前面是这次申请的内存块,后面是剩余的内存块。
剩余的内存块的起始位置用于储存内存块的entry信息,初始化used和d_size属性,未被使用,并更新剩余内存块的大小。
至此,内存申请就完成了。
2|释放内存
释放内存,由如下函数实现:
/**
* Free an allocated data
* @param data pointer to an allocated memory
*/
void ug_mem_free(const void * data)
{
if(data == &zero_mem) return;
if(data == NULL) return;
#if UG_MEM_ADD_JUNK
_ug_memset((void *)data, 0xbb, _ug_mem_get_size(data));
#endif
#if UG_ENABLE_GC == 0
/*e points to the header*/
ug_mem_ent_t * e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)((uint8_t *)data - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t));
e->header.s.used = 0;
#endif
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
#if UG_MEM_AUTO_DEFRAG
static uint16_t full_defrag_cnt = 0;
full_defrag_cnt++;
if(full_defrag_cnt < UG_MEM_FULL_DEFRAG_CNT) {
/* Make a simple defrag.
* Join the following free entries after this*/
ug_mem_ent_t * e_next;
e_next = ent_get_next(e);
while(e_next != NULL) {
if(e_next->header.s.used == 0) {
e->header.s.d_size += e_next->header.s.d_size + sizeof(e->header);
}
else {
break;
}
e_next = ent_get_next(e_next);
}
}
else {
full_defrag_cnt = 0;
ug_mem_defrag();
}
#endif /*UG_MEM_AUTO_DEFRAG*/
#else /*Use custom, user defined free function*/
#if UG_ENABLE_GC == 0
UG_MEM_CUSTOM_FREE(e);
#else
UG_MEM_CUSTOM_FREE((void *)data);
#endif /*UG_ENABLE_GC*/
#endif
}主体内容先获取改内存块的入口地址,将used 属性设为0,表示未被使用。
#if UG_MEM_ADD_JUNK
_ug_memset((void *)data, 0xbb, _ug_mem_get_size(data));
#endif上面部分用宏定义决定是否需要添加无效数据到将释放的内存块。
#if UG_MEM_AUTO_DEFRAG
static uint16_t full_defrag_cnt = 0;
full_defrag_cnt++;
if(full_defrag_cnt < UG_MEM_FULL_DEFRAG_CNT) {
/* Make a simple defrag.
* Join the following free entries after this*/
ug_mem_ent_t * e_next;
e_next = ent_get_next(e);
while(e_next != NULL) {
if(e_next->header.s.used == 0) {
e->header.s.d_size += e_next->header.s.d_size + sizeof(e->header);
}
else {
break;
}
e_next = ent_get_next(e_next);
}
}
else {
full_defrag_cnt = 0;
ug_mem_defrag();
}
#endif /*UG_MEM_AUTO_DEFRAG*/上面部分,用宏定义决定是否开启自动合并未被使用的内存块。
用静态变量full_defrag_cnt 统计释放过的内存块数,如果次数小于宏UG_MEM_FULL_DEFRAG_CNT 则执行简单的块合并 (即碎片整理),如果超过,则执行函数ug_mem_defrag()。
简单的合并,即循环寻找下一个内存块入口,如果该内存块,未被使用,则合并到此次释放的内存块中。如果下一个内存块,已经被使用,则跳出。
ug_mem_defrag() 会合并整个内存池中所有相连的可用内存块, 如下:
/**
* Join the adjacent free memory blocks
*/
void ug_mem_defrag(void)
{
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
ug_mem_ent_t * e_free;
ug_mem_ent_t * e_next;
e_free = ent_get_next(NULL);
while(1) {
/*Search the next free entry*/
while(e_free != NULL) {
if(e_free->header.s.used != 0) {
e_free = ent_get_next(e_free);
}
else {
break;
}
}
if(e_free == NULL) return;
/*Joint the following free entries to the free*/
e_next = ent_get_next(e_free);
while(e_next != NULL) {
if(e_next->header.s.used == 0) {
e_free->header.s.d_size += e_next->header.s.d_size + sizeof(e_next->header);
}
else {
break;
}
e_next = ent_get_next(e_next);
}
if(e_next == NULL) return;
/*Continue from the lastly checked entry*/
e_free = e_next;
}
#endif
}第一个大循环首先循环寻找一个可用内存块,然后判断该内存块后紧接的内存块是否可用,如果可用则合并,直到没有相邻的内存块可以合并。然后开始下一轮的大循环,以此往复,合并所有相连的可用内存块。
3|内存重申请
/**
* Reallocate a memory with a new size. The old content will be kept.
* @param data pointer to an allocated memory.
* Its content will be copied to the new memory block and freed
* @param new_size the desired new size in byte
* @return pointer to the new memory
*/
void * ug_mem_realloc(void * data_p, size_t new_size)
{
#ifdef UG_ARCH_64
/*Round the size up to 8*/
new_size = (new_size + 7) & (~0x7);
#else
/*Round the size up to 4*/
new_size = (new_size + 3) & (~0x3);
#endif
/*data_p could be previously freed pointer (in this case it is invalid)*/
if(data_p != NULL) {
ug_mem_ent_t * e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)((uint8_t *)data_p - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t));
if(e->header.s.used == 0) {
data_p = NULL;
}
}
uint32_t old_size = _ug_mem_get_size(data_p);
if(old_size == new_size) return data_p; /*Also avoid reallocating the same memory*/
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
/* Truncate the memory if the new size is smaller. */
if(new_size < old_size) {
ug_mem_ent_t * e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)((uint8_t *)data_p - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t));
ent_trunc(e, new_size);
return &e->first_data;
}
#endif
void * new_p;
new_p = ug_mem_alloc(new_size);
if(new_p == NULL) {
//UG_LOG_WARN("Couldn't allocate memory");
return NULL;
}
if(data_p != NULL) {
/*Copy the old data to the new. Use the smaller size*/
if(old_size != 0) {
_ug_memcpy(new_p, data_p, UG_MATH_MIN(new_size, old_size));
ug_mem_free(data_p);
}
}
return new_p;
}内存重申请,通过判断需要重申请的大小与原内存块的大小,如果需要重申请的大小小于原内存块的大小,直接根据需要重申请的大小截断原内存块。如果重申请的大小大于原内存块,则新申请一个大小为重申请的小,并且拷贝原内存块的数据至新的内存块,然后释放原内存块。
四、源码
整个动态内存申请的源码如下:
File “ug_mem.h”
#ifndef __UG_MEM_H__
#define __UG_MEM_H__
#include <stdint.h>
//#include "UVGUI.h"
#include <string.h>
#include "ug_type.h"
/*********************
* DEFINES
*********************/
//#define UG_TEMPORAL_BUF
#ifndef UG_MEM_BUF_MAX_NUM
#define UG_MEM_BUF_MAX_NUM 16
#endif
/**********************
* TYPEDEFS
**********************/
/**
* Heap information structure.
*/
typedef struct {
uint32_t total_size; /**< Total heap size */
uint32_t free_cnt;
uint32_t free_size; /**< Size of available memory */
uint32_t free_biggest_size;
uint32_t used_cnt;
uint32_t max_used; /**< Max size of Heap memory used */
uint8_t used_pct; /**< Percentage used */
uint8_t frag_pct; /**< Amount of fragmentation */
} ug_mem_monitor_t;
typedef struct {
void * p;
uint16_t size;
uint8_t used : 1;
} ug_mem_buf_t;
typedef ug_mem_buf_t ug_mem_buf_arr_t[UG_MEM_BUF_MAX_NUM];
extern ug_mem_buf_arr_t _ug_mem_buf;
/**********************
* GLOBAL PROTOTYPES
**********************/
/**
* Initialize the dyn_mem module (work memory and other variables)
*/
void _ug_mem_init(void);
/**
* Clean up the memory buffer which frees all the allocated memories.
* @note It work only if `UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0`
*/
void _ug_mem_deinit(void);
/**
* Allocate a memory dynamically
* @param size size of the memory to allocate in bytes
* @return pointer to the allocated memory
*/
void * ug_mem_alloc(size_t size);
/**
* Free an allocated data
* @param data pointer to an allocated memory
*/
void ug_mem_free(const void * data);
/**
* Reallocate a memory with a new size. The old content will be kept.
* @param data pointer to an allocated memory.
* Its content will be copied to the new memory block and freed
* @param new_size the desired new size in byte
* @return pointer to the new memory
*/
void * ug_mem_realloc(void * data_p, size_t new_size);
/**
* Join the adjacent free memory blocks
*/
void ug_mem_defrag(void);
/**
*
* @return
*/
ug_res_t ug_mem_test(void);
/**
* Give information about the work memory of dynamic allocation
* @param mon_p pointer to a dm_mon_p variable,
* the result of the analysis will be stored here
*/
void ug_mem_monitor(ug_mem_monitor_t * mon_p);
/**
* Give the size of an allocated memory
* @param data pointer to an allocated memory
* @return the size of data memory in bytes
*/
uint32_t _ug_mem_get_size(const void * data);
#ifdef UG_TEMPORAL_BUF
/**
* Get a temporal buffer with the given size.
* @param size the required size
*/
void * _ug_mem_buf_get(uint32_t size);
/**
* Release a memory buffer
* @param p buffer to release
*/
void _ug_mem_buf_release(void * p);
/**
* Free all memory buffers
*/
void _ug_mem_buf_free_all(void);
#endif
//! @cond Doxygen_Suppress
/**
* Same as `memcpy` but optimized for 4 byte operation.
* @param dst pointer to the destination buffer
* @param src pointer to the source buffer
* @param len number of byte to copy
*/
void * _ug_memcpy(void * dst, const void * src, size_t len);
/**
* Same as `memcpy` but optimized to copy only a few bytes.
* @param dst pointer to the destination buffer
* @param src pointer to the source buffer
* @param len number of byte to copy
*/
static inline void * _ug_memcpy_small(void * dst, const void * src, size_t len)
{
uint8_t * d8 = (uint8_t *)dst;
const uint8_t * s8 = (const uint8_t *)src;
while(len) {
*d8 = *s8;
d8++;
s8++;
len--;
}
return dst;
}
void _ug_memset_00(void * dst, size_t len);
void _ug_memset(void * dst, uint8_t v, size_t len);
void * _ug_memcpy(void * dst, const void * src, size_t len);
#endif // !__UG_MEM_H__File “ug_mem.c”
#include "ug_mem.h"
#include "ug_type.h"
#include "ug_math.h"
#include "ug_draw_blend.h"
#include "ug_user_config.h"
#include <string.h>
/**********************
* MACROS
**********************/
#define COPY32 *d32 = *s32; d32++; s32++;
#define COPY8 *d8 = *s8; d8++; s8++;
#define SET32(x) *d32 = x; d32++;
#define REPEAT8(expr) expr expr expr expr expr expr expr expr
#define ALIGN_MASK 0x3
#ifdef UG_ARCH_64
#define MEM_UNIT uint64_t
#else
#define MEM_UNIT uint32_t
#endif
#ifndef UG_MEM_FULL_DEFRAG_CNT
#define UG_MEM_FULL_DEFRAG_CNT 16
#endif
#define MEM_BUF_SMALL_SIZE 16
/**********************
* Typedef
**********************/
/*The size of this union must be 4 bytes (uint32_t)*/
typedef union {
struct {
MEM_UNIT used : 1; /* 1: if the entry is used*/
MEM_UNIT d_size : 31; /* Size off the data (in bytes)*/
} s;
MEM_UNIT header; /* The header (used + d_size)*/
} ug_mem_header_t;
typedef struct {
ug_mem_header_t header;
uint8_t first_data; /*First data byte in the allocated data (Just for easily create a pointer)*/
} ug_mem_ent_t;
/**********************
* STATIC PROTOTYPES
**********************/
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
static ug_mem_ent_t * ent_get_next(ug_mem_ent_t * act_e);
static void * ent_alloc(ug_mem_ent_t * e, size_t size);
static void ent_trunc(ug_mem_ent_t * e, size_t size);
#endif
/**********************
* STATIC VARIABLES
**********************/
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
static uint8_t * work_mem;
#endif
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
static uint32_t mem_max_size; /*Tracks the maximum total size of memory ever used from the internal heap*/
#endif
static uint32_t zero_mem; /*Give the address of this variable if 0 byte should be allocated*/
#ifdef UG_TEMPORAL_BUF
static uint8_t mem_buf1_32[MEM_BUF_SMALL_SIZE];
static uint8_t mem_buf2_32[MEM_BUF_SMALL_SIZE];
static ug_mem_buf_t mem_buf_small[] = {
{.p = mem_buf1_32, .size = MEM_BUF_SMALL_SIZE, .used = 0},
{.p = mem_buf2_32, .size = MEM_BUF_SMALL_SIZE, .used = 0}
};
#endif // UG_TEMPORAL_BUF
/**********************
* GLOBAL FUNCTIONS
**********************/
/**
* Initialize the dyn_mem module (work memory and other variables)
*/
void _ug_mem_init(void)
{
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
/*Allocate a large array to store the dynamically allocated data*/
static UG_MEM_ATTR MEM_UNIT work_mem_int[UG_MEM_SIZE / sizeof(MEM_UNIT)];
work_mem = (uint8_t *)work_mem_int;
mem_max_size = 0;
ug_mem_ent_t * full = (ug_mem_ent_t *)work_mem;
full->header.s.used = 0;
/*The total mem size id reduced by the first header and the close patterns */
full->header.s.d_size = UG_MEM_SIZE - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t);
#endif
}
/**
* Clean up the memory buffer which frees all the allocated memories.
* @note It work only if `UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0`
*/
void _ug_mem_deinit(void)
{
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
_ug_memset_00(work_mem, (UG_MEM_SIZE / sizeof(MEM_UNIT)) * sizeof(MEM_UNIT));
ug_mem_ent_t * full = (ug_mem_ent_t *)work_mem;
full->header.s.used = 0;
/*The total mem size id reduced by the first header and the close patterns */
full->header.s.d_size = UG_MEM_SIZE - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t);
#endif
}
/**
* Allocate a memory dynamically
* @param size size of the memory to allocate in bytes
* @return pointer to the allocated memory
*/
void * ug_mem_alloc(size_t size)
{
if(size == 0) {
return &zero_mem;
}
#ifdef UG_ARCH_64
/*Round the size up to 8*/
size = (size + 7) & (~0x7);
#else
/*Round the size up to 4*/
size = (size + 3) & (~0x3);
#endif
void * alloc = NULL;
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
/*Use the built-in allocators*/
ug_mem_ent_t * e = NULL;
/* Search for a appropriate entry*/
do {
/* Get the next entry*/
e = ent_get_next(e);
/*If there is next entry then try to allocate there*/
if(e != NULL) {
alloc = ent_alloc(e, size);
}
/* End if there is not next entry OR the alloc. is successful*/
} while(e != NULL && alloc == NULL);
#endif /* UG_MEM_CUSTOM */
if(alloc == NULL) {
//TODO: LOG("Couldn't allocate memory");
}
else {
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
/* just a safety check, should always be true */
if((uintptr_t) alloc > (uintptr_t) work_mem) {
if((((uintptr_t) alloc - (uintptr_t) work_mem) + size) > mem_max_size) {
mem_max_size = ((uintptr_t) alloc - (uintptr_t) work_mem) + size;
}
}
#endif
}
return alloc;
}
/**
* Free an allocated data
* @param data pointer to an allocated memory
*/
void ug_mem_free(const void * data)
{
if(data == &zero_mem) return;
if(data == NULL) return;
#if UG_MEM_ADD_JUNK
_ug_memset((void *)data, 0xbb, _ug_mem_get_size(data));
#endif
#if UG_ENABLE_GC == 0
/*e points to the header*/
ug_mem_ent_t * e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)((uint8_t *)data - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t));
e->header.s.used = 0;
#endif
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
#if UG_MEM_AUTO_DEFRAG
static uint16_t full_defrag_cnt = 0;
full_defrag_cnt++;
if(full_defrag_cnt < UG_MEM_FULL_DEFRAG_CNT) {
/* Make a simple defrag.
* Join the following free entries after this*/
ug_mem_ent_t * e_next;
e_next = ent_get_next(e);
while(e_next != NULL) {
if(e_next->header.s.used == 0) {
e->header.s.d_size += e_next->header.s.d_size + sizeof(e->header);
}
else {
break;
}
e_next = ent_get_next(e_next);
}
}
else {
full_defrag_cnt = 0;
ug_mem_defrag();
}
#endif /*UG_MEM_AUTO_DEFRAG*/
#else /*Use custom, user defined free function*/
#if UG_ENABLE_GC == 0
UG_MEM_CUSTOM_FREE(e);
#else
UG_MEM_CUSTOM_FREE((void *)data);
#endif /*UG_ENABLE_GC*/
#endif
}
/**
* Reallocate a memory with a new size. The old content will be kept.
* @param data pointer to an allocated memory.
* Its content will be copied to the new memory block and freed
* @param new_size the desired new size in byte
* @return pointer to the new memory
*/
#if UG_ENABLE_GC == 0
void * ug_mem_realloc(void * data_p, size_t new_size)
{
#ifdef UG_ARCH_64
/*Round the size up to 8*/
new_size = (new_size + 7) & (~0x7);
#else
/*Round the size up to 4*/
new_size = (new_size + 3) & (~0x3);
#endif
/*data_p could be previously freed pointer (in this case it is invalid)*/
if(data_p != NULL) {
ug_mem_ent_t * e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)((uint8_t *)data_p - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t));
if(e->header.s.used == 0) {
data_p = NULL;
}
}
uint32_t old_size = _ug_mem_get_size(data_p);
if(old_size == new_size) return data_p; /*Also avoid reallocating the same memory*/
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
/* Truncate the memory if the new size is smaller. */
if(new_size < old_size) {
ug_mem_ent_t * e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)((uint8_t *)data_p - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t));
ent_trunc(e, new_size);
return &e->first_data;
}
#endif
void * new_p;
new_p = ug_mem_alloc(new_size);
if(new_p == NULL) {
//UG_LOG_WARN("Couldn't allocate memory");
return NULL;
}
if(data_p != NULL) {
/*Copy the old data to the new. Use the smaller size*/
if(old_size != 0) {
_ug_memcpy(new_p, data_p, UG_MATH_MIN(new_size, old_size));
ug_mem_free(data_p);
}
}
return new_p;
}
#else /* UG_ENABLE_GC */
void * ug_mem_realloc(void * data_p, size_t new_size)
{
void * new_p = UG_MEM_CUSTOM_REALLOC(data_p, new_size);
if(new_p == NULL) UG_LOG_WARN("Couldn't allocate memory");
return new_p;
}
#endif /* ug_enable_gc */
/**
* Join the adjacent free memory blocks
*/
void ug_mem_defrag(void)
{
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
ug_mem_ent_t * e_free;
ug_mem_ent_t * e_next;
e_free = ent_get_next(NULL);
while(1) {
/*Search the next free entry*/
while(e_free != NULL) {
if(e_free->header.s.used != 0) {
e_free = ent_get_next(e_free);
}
else {
break;
}
}
if(e_free == NULL) return;
/*Joint the following free entries to the free*/
e_next = ent_get_next(e_free);
while(e_next != NULL) {
if(e_next->header.s.used == 0) {
e_free->header.s.d_size += e_next->header.s.d_size + sizeof(e_next->header);
}
else {
break;
}
e_next = ent_get_next(e_next);
}
if(e_next == NULL) return;
/*Continue from the lastly checked entry*/
e_free = e_next;
}
#endif
}
ug_res_t ug_mem_test(void)
{
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
ug_mem_ent_t * e;
e = ent_get_next(NULL);
while(e) {
if(e->header.s.d_size > UG_MEM_SIZE) {
return UG_RES_INV;
}
uint8_t * e8 = (uint8_t *) e;
if(e8 + e->header.s.d_size > work_mem + UG_MEM_SIZE) {
return UG_RES_INV;
}
e = ent_get_next(e);
}
#endif
return UG_RES_OK;
}
/**
* Give information about the work memory of dynamic allocation
* @param mon_p pointer to a dm_mon_p variable,
* the result of the analysis will be stored here
*/
void ug_mem_monitor(ug_mem_monitor_t * mon_p)
{
/*Init the data*/
_ug_memset(mon_p, 0, sizeof(ug_mem_monitor_t));
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
ug_mem_ent_t * e;
e = NULL;
e = ent_get_next(e);
while(e != NULL) {
if(e->header.s.used == 0) {
mon_p->free_cnt++;
mon_p->free_size += e->header.s.d_size;
if(e->header.s.d_size > mon_p->free_biggest_size) {
mon_p->free_biggest_size = e->header.s.d_size;
}
}
else {
mon_p->used_cnt++;
}
e = ent_get_next(e);
}
mon_p->total_size = UG_MEM_SIZE;
mon_p->max_used = mem_max_size;
mon_p->used_pct = 100 - (100U * mon_p->free_size) / mon_p->total_size;
if(mon_p->free_size > 0) {
mon_p->frag_pct = (uint32_t)mon_p->free_biggest_size * 100U / mon_p->free_size;
mon_p->frag_pct = 100 - mon_p->frag_pct;
}
else {
mon_p->frag_pct = 0; /*no fragmentation if all the RAM is used*/
}
#endif
}
/**
* Give the size of an allocated memory
* @param data pointer to an allocated memory
* @return the size of data memory in bytes
*/
#if UG_ENABLE_GC == 0
uint32_t _ug_mem_get_size(const void * data)
{
if(data == NULL) return 0;
if(data == &zero_mem) return 0;
ug_mem_ent_t * e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)((uint8_t *)data - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t));
return e->header.s.d_size;
}
#else /* UG_ENABLE_GC */
uint32_t _ug_mem_get_size(const void * data)
{
return UG_MEM_CUSTOM_GET_SIZE(data);
}
#endif /*UG_ENABLE_GC*/
#ifdef UG_TEMPORAL_BUF
/**
* Get a temporal buffer with the given size.
* @param size the required size
*/
void * _ug_mem_buf_get(uint32_t size)
{
if(size == 0) return NULL;
/*Try small static buffers first*/
uint8_t i;
if(size <= MEM_BUF_SMALL_SIZE) {
for(i = 0; i < sizeof(mem_buf_small) / sizeof(mem_buf_small[0]); i++) {
if(mem_buf_small[i].used == 0) {
mem_buf_small[i].used = 1;
return mem_buf_small[i].p;
}
}
}
/*Try to find a free buffer with suitable size */
int8_t i_guess = -1;
for(i = 0; i < UG_MEM_BUF_MAX_NUM; i++) {
if(UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).used == 0 && UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).size >= size) {
if(UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).size == size) {
UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).used = 1;
return UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).p;
}
else if(i_guess < 0) {
i_guess = i;
}
/*If size of `i` is closer to `size` prefer it*/
else if(UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).size < UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i_guess]).size) {
i_guess = i;
}
}
}
if(i_guess >= 0) {
UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i_guess]).used = 1;
return UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i_guess]).p;
}
/*Reallocate a free buffer*/
for(i = 0; i < UG_MEM_BUF_MAX_NUM; i++) {
if(UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).used == 0) {
UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).used = 1;
UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).size = size;
/*if this fails you probably need to increase your UG_MEM_SIZE/heap size*/
UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).p = ug_mem_realloc(UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).p, size);
if(UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).p == NULL) {
UG_DEBUG_ASSERT(false, "Out of memory, can't allocate a new buffer (increase your UG_MEM_SIZE/heap size", 0x00);
}
return UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).p;
}
}
UG_DEBUG_ASSERT(false, "No free buffer. Increase UG_DRAW_BUF_MAX_NUM.", 0x00);
return NULL;
}
/**
* Release a memory buffer
* @param p buffer to release
*/
void _ug_mem_buf_release(void * p)
{
uint8_t i;
/*Try small static buffers first*/
for(i = 0; i < sizeof(mem_buf_small) / sizeof(mem_buf_small[0]); i++) {
if(mem_buf_small[i].p == p) {
mem_buf_small[i].used = 0;
return;
}
}
for(i = 0; i < UG_MEM_BUF_MAX_NUM; i++) {
if(UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).p == p) {
UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).used = 0;
return;
}
}
UG_LOG_ERROR("ug_mem_buf_release: p is not a known buffer")
}
/**
* Free all memory buffers
*/
void _ug_mem_buf_free_all(void)
{
uint8_t i;
for(i = 0; i < sizeof(mem_buf_small) / sizeof(mem_buf_small[0]); i++) {
mem_buf_small[i].used = 0;
}
for(i = 0; i < UG_MEM_BUF_MAX_NUM; i++) {
if(UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).p) {
ug_mem_free(UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).p);
UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).p = NULL;
UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).used = 0;
UG_GC_ROOT(_ug_mem_buf[i]).size = 0;
}
}
}
#endif
/**
* Same as `memset` but optimized for 4 byte operation.
* `dst` should be word aligned else normal `memcpy` will be used
* @param dst pointer to the destination buffer
* @param v value to set [0..255]
* @param len number of byte to set
*/
void _ug_memset(void * dst, uint8_t v, size_t len)
{
uint8_t * d8 = (uint8_t *) dst;
uintptr_t d_align = (ug_uintptr_t) d8 & ALIGN_MASK;
/*Make the address aligned*/
if(d_align) {
d_align = ALIGN_MASK + 1 - d_align;
while(d_align && len) {
*d8 = v;
d8++;
len--;
d_align--;
}
}
uint32_t v32 = v + (v << 8) + (v << 16) + (v << 24);
uint32_t * d32 = (uint32_t *)d8;
while(len > 32) {
SET32(v32);
SET32(v32);
SET32(v32);
SET32(v32);
SET32(v32);
SET32(v32);
SET32(v32);
SET32(v32);
len -= 32;
}
while(len > 4) {
SET32(v32);
len -= 4;
}
d8 = (uint8_t *)d32;
while(len) {
*d8 = v;
d8++;
len--;
}
}
/**
* Same as `memset(dst, 0x00, len)` but optimized for 4 byte operation.
* `dst` should be word aligned else normal `memcpy` will be used
* @param dst pointer to the destination buffer
* @param len number of byte to set
*/
void _ug_memset_00(void * dst, size_t len)
{
uint8_t * d8 = (uint8_t *) dst;
uintptr_t d_align = (ug_uintptr_t) d8 & ALIGN_MASK;
/*Make the address aligned*/
if(d_align) {
d_align = ALIGN_MASK + 1 - d_align;
while(d_align && len) {
*d8 = 0x00;
d8++;
len--;
d_align--;
}
}
uint32_t * d32 = (uint32_t *)d8;
while(len > 32) {
SET32(0);
SET32(0);
SET32(0);
SET32(0);
SET32(0);
SET32(0);
SET32(0);
SET32(0);
len -= 32;
}
while(len > 4) {
SET32(0);
len -= 4;
}
d8 = (uint8_t *)d32;
while(len) {
*d8 = 0;
d8++;
len--;
}
}
/**
* Same as `memcpy` but optimized for 4 byte operation.
* @param dst pointer to the destination buffer
* @param src pointer to the source buffer
* @param len number of byte to copy
*/
void * _ug_memcpy(void * dst, const void * src, size_t len)
{
uint8_t * d8 = dst;
const uint8_t * s8 = src;
ug_uintptr_t d_align = (ug_uintptr_t)d8 & ALIGN_MASK;
ug_uintptr_t s_align = (ug_uintptr_t)s8 & ALIGN_MASK;
/*Byte copy for unaligned memories*/
if(s_align != d_align) {
while(len > 32) {
REPEAT8(COPY8);
REPEAT8(COPY8);
REPEAT8(COPY8);
REPEAT8(COPY8);
len -= 32;
}
while(len) {
COPY8
len--;
}
return dst;
}
/*Make the memories aligned*/
if(d_align) {
d_align = ALIGN_MASK + 1 - d_align;
while(d_align && len) {
COPY8;
d_align--;
len--;
}
}
uint32_t * d32 = (uint32_t *)d8;
const uint32_t * s32 = (uint32_t *)s8;
while(len > 32) {
REPEAT8(COPY32)
len -= 32;
}
while(len > 4) {
COPY32;
len -= 4;
}
d8 = (uint8_t *)d32;
s8 = (const uint8_t *)s32;
while(len) {
COPY8
len--;
}
return dst;
}
/**
* Same as `memset(dst, 0xFF, len)` but optimized for 4 byte operation.
* `dst` should be word aligned else normal `memcpy` will be used
* @param dst pointer to the destination buffer
* @param len number of byte to set
*/
void _ug_memset_ff(void * dst, size_t len)
{
uint8_t * d8 = (uint8_t *) dst;
uintptr_t d_align = (ug_uintptr_t) d8 & ALIGN_MASK;
/*Make the address aligned*/
if(d_align) {
d_align = ALIGN_MASK + 1 - d_align;
while(d_align && len) {
*d8 = 0xFF;
d8++;
len--;
d_align--;
}
}
uint32_t * d32 = (uint32_t *)d8;
while(len > 32) {
SET32(0xFFFFFFFF);
SET32(0xFFFFFFFF);
SET32(0xFFFFFFFF);
SET32(0xFFFFFFFF);
SET32(0xFFFFFFFF);
SET32(0xFFFFFFFF);
SET32(0xFFFFFFFF);
SET32(0xFFFFFFFF);
len -= 32;
}
while(len > 4) {
SET32(0xFFFFFFFF);
len -= 4;
}
d8 = (uint8_t *)d32;
while(len) {
*d8 = 0xFF;
d8++;
len--;
}
}
/**********************
* STATIC FUNCTIONS
**********************/
#if UG_MEM_CUSTOM == 0
/**
* Give the next entry after 'act_e'
* @param act_e pointer to an entry
* @return pointer to an entry after 'act_e'
*/
static ug_mem_ent_t * ent_get_next(ug_mem_ent_t * act_e)
{
ug_mem_ent_t * next_e = NULL;
if(act_e == NULL) { /*NULL means: get the first entry*/
next_e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)work_mem;
}
else { /*Get the next entry */
uint8_t * data = &act_e->first_data;
next_e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)&data[act_e->header.s.d_size];
if(&next_e->first_data >= &work_mem[UG_MEM_SIZE]) next_e = NULL;
}
return next_e;
}
/**
* Try to do the real allocation with a given size
* @param e try to allocate to this entry
* @param size size of the new memory in bytes
* @return pointer to the allocated memory or NULL if not enough memory in the entry
*/
static void * ent_alloc(ug_mem_ent_t * e, size_t size)
{
void * alloc = NULL;
/*If the memory is free and big enough then use it */
if(e->header.s.used == 0 && e->header.s.d_size >= size) {
/*Truncate the entry to the desired size */
ent_trunc(e, size);
e->header.s.used = 1;
/*Save the allocated data*/
alloc = &e->first_data;
}
return alloc;
}
/**
* Truncate the data of entry to the given size
* @param e Pointer to an entry
* @param size new size in bytes
*/
static void ent_trunc(ug_mem_ent_t * e, size_t size)
{
#ifdef UG_ARCH_64
/*Round the size up to 8*/
size = (size + 7) & (~0x7);
#else
/*Round the size up to 4*/
size = (size + 3) & (~0x3);
#endif
/*Don't let empty space only for a header without data.
如果分配后只剩仅能保存一个头部的内存,那么就直接全部分配给这个内存块*/
if(e->header.s.d_size == size + sizeof(ug_mem_header_t)) {
size = e->header.s.d_size;
}
/* Create the new entry after the current if there is space for it */
if(e->header.s.d_size != size) {
uint8_t * e_data = &e->first_data;
ug_mem_ent_t * after_new_e = (ug_mem_ent_t *)&e_data[size];
after_new_e->header.s.used = 0;
after_new_e->header.s.d_size = (uint32_t)e->header.s.d_size - size - sizeof(ug_mem_header_t);
}
/* Set the new size for the original entry */
e->header.s.d_size = (uint32_t)size;
}
#endif
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!